Rate Of Reaction From Graph
How does the temperature impact the rate of a chemic reaction?
Effect of temperature on the rate of reaction:
- When the temperature increases, the charge per unit of reaction also increases.
- (a) For instance, two sets of experiments are carried out using the reacting weather below:
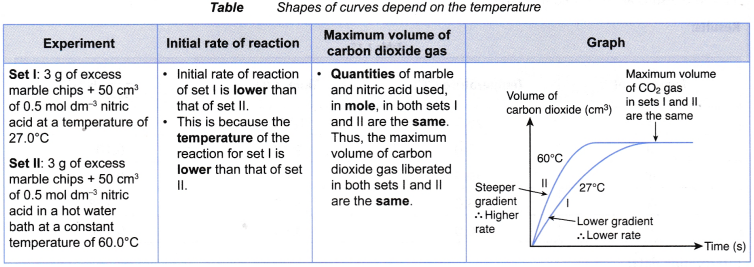
Set I: 1 yard of granulated zinc and 20 cmthree of 0.two mol dm– 3 hydrochloric acid at threescore°C
Set Ii: ane g of granulated zinc and 20 cmthree of 0.2 mol dm– 3 hydrochloric acid at 30°C
(b) The rate of reaction of prepare I is college than that of fix Ii.
(c) This is because the temperature (lx°C) of the reacting mixture in set I is college than the temperature (thirty°C) of the reacting mixutre in set II. - When investigating experimentally the upshot of temperature on the rate of reaction,
- the experiment is repeated a few times, each time using a unlike temperature of a reactant.
- all the other factors/weather condition are kept constant in all the experiments.
- The following shows an instance of the result of temperature on the rate of reaction. Tabular array shows the method to derive the shapes of curves plotted for two sets of experiments.
People also ask
- What is the charge per unit of the reaction?
- How do you summate the reaction rate?
- What factors bear on the rate of a reaction?
- How does the surface surface area touch on the rate of reaction?
- Explain the effect of concentration on the charge per unit of reaction?
- What is the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction?
- What is the collision theory in chemical science?
- How does the standoff theory affect the rate of reaction?
Event of temperature on rate of reaction experiment
Aim: To investigate the issue of temperature on the rate of reaction.
Problem statement: How does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
Hypothesis: An increase in temperature will increase the rate of reaction.
Variables:
(a) Manipulated variable : Temperature ot sodium thiosulphate solution
(b) Responding variable : Rate of reaction
(c) Controlled variables : Volume and concentration of sodium thiosulphate solution, volume and concentration of sulphuric acrid, size of conical flask
Operational definition:
Charge per unit of reaction is inversely proportional to the time taken for the marker 'X' to disappear from sight.

Materials: 0.ii mol dm– three sodium thiosulphate solution, 1 mol dm– 3 sulphuric acid, white paper with a marker 'X' at the centre.
Appliance: 150 cm3 conical flasks, l cmthree measuring cylinder, ten cm– 3 measuring cylinder, digital stopwatch (electronically operated with an accuracy of 0.01 s), thermometer, Bunsen burner, tripod stand, wire gauze.
Procedure:

- 50 cmiii of 0.2 mol dm– 3 sodium thiosulphate solution is measured using a measuring cylinder and poured into a conical flask.
- The temperature of this solution is measured using a thermometer.
- The conical flask is placed on height of a piece of white newspaper with a marking 'X' at the centre.
- 5 cm3 of 1 mol dm– 3 sulphuric acid is measured using a ten cm3 measuring cylinder.
- The sulphuric acid is then poured quickly and carefully into the conical flask and a stopwatch is started immediately.
- The mixture in the conical flask is swirled a few times. The conical flask is then placed back on the white paper.
- The marker 'X' is viewed vertically from the top through the solution, as shown in Effigy.
- The stopwatch is stopped immediately once the mark 'X' disappears from sight.
- The time f required for the marking '10' to disappear from sight is recorded.
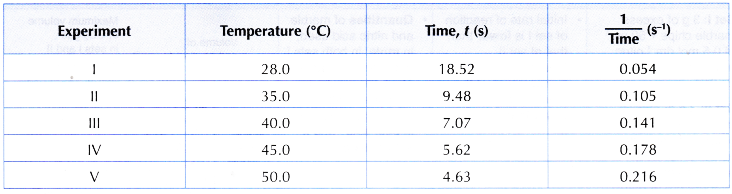
- Steps one to 9 are repeated using fifty cmthree of 0.2 mol dm– 3 sodium thiosulphate solution at 35°C, 40°C, 45°C and 50°C respectively by heating the solution as shown in Effigy before 5 cm3 of 1 mol dm– 3 sulphuric acid is added. All other conditions remain unchanged.
- The results are recorded in a table.
Results:
Interpreting information:
1. Based on the results, two graphs are plotted.
(a) Graph I: Graph of the temperature against time
(b) Graph Ii: Graph of the temperature against i/fourth dimension
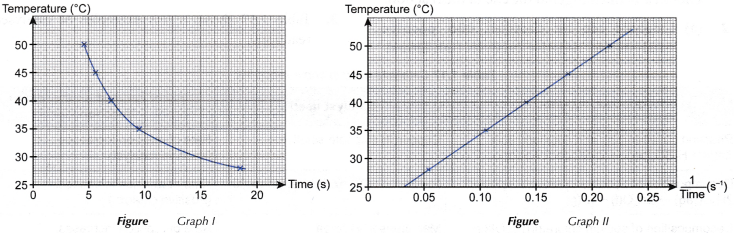
two.From graph I, it can be deduced that as the temperature increases, the time taken for the marker 'X' to disappear from sight becomes shorter.
3. From graph Ii, it tin can exist deduced that the temperature increases linearly with 1/fourth dimension.
Discussion:
- (a) From the graphs plotted, the following inference can exist deduced:
"Temperature increases linearly with 1/time"
(b) But, rate of reaction ∝ 1/time.
(c) Hence, rate of reaction increases linearly with temperature. - In other words, as the temperature increases, the charge per unit of reaction also increases.
- Commonly, the rate of a reaction approximately doubles for every ten°C rise in temperature.
- The concentration and book of both sodium thiosulphate solution and sulphuric acid are kept constant in each set of the experiment. Whatever change in charge per unit of reaction is due to the deviation in temperature.
Determination:
Rate of reaction increases when the temperature of the reaction increases. Hence, the hypothesis can exist accustomed.
Rate Of Reaction From Graph,
Source: https://www.aplustopper.com/temperature-affect-rate-chemical-reaction/
Posted by: lightliess1983.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Rate Of Reaction From Graph"
Post a Comment